
α-radiation can be stopped by a sheet of paper. The atomic number of an α-particle is Z=2, so the atomic number of the decaying nucleus is decreased by two during an α-decay and a different element is created. An α-particle is the nucleus of a helium atom, helium-4, which consists of two protons and two neutrons. When an atomic nucleus transforms into a different element by emitting an α-particle. In 1899 Ernest Rutherford named alpha (α), beta (β), and gamma (γ) radiation, after the first three letters of the Greek alphabet. The different types of radiation can be identified by their ability to pass through matter. Radioactivity is the spontaneous decay of an unstable atom through the emission, from the atomic nucleus, of a particle of ionising radiation. There are less than 300 stable nuclei and over 3,000 unstable radioactive nuclei.
carbon-14, the radioactive isotope used in carbon dating, has Z=6 and N=8.the stable isotope carbon-12, the most common type of carbon in the human body, has Z=6 and N=6.
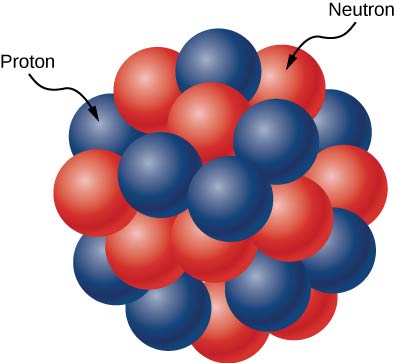
The ‘atomic mass’ of the nucleus is given by A=Z+N, where N is the number of neutrons in the nucleus.ĭifferent isotopes of an element have different numbers of neutrons in their nucleus. The element oxygen has an atomic number Z=8, while carbon has Z=6. The chemical element of an atom is determined by the number of protons, also known as the ‘atomic number (Z)’ of the nucleus. Protons and neutrons are in turn made up of particles called quarks. The nucleus is a collection of particles called protons, which are positively charged, and neutrons, which are electrically neutral. They contain more than 99.9% of the mass of an atom and are ten thousand times smaller than an atom! Nuclei are very dense and extremely small. Nuclear physics research tries to answer the fundamental questions:Ītoms are made up of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
